A durian orchard in Pahang
is directed to achieving a profitable crop of fruits in a growing season.
A "durian crop production cycle" generally refers to the sequence of vegetative growth and reproductive development processes of the durian trees and how the farmer manipulates these processes that have an effect on fruit production and quality in a growing season.
When all the fruits is harvested, the durian season for that period of time is considered complete and over. This is also the beginning of another new growing season.
Durian crop production is the procedure or how a farmer manages his durian orchard to improve plant growth, flowering, fruit set, fruit growth and fruit development with the goal of improving the quantity and quality of durian fruits produced. How the farmer promotes synchronization and early fruiting to facilitate marketing strategy is also included in this procedure.
Durian orchard management includes many farm activities and the use of production materials. Some of these activities are pruning, irrigation, fertilizer applications, pests and disease control, flower thinning, assisted pollination, fruit thinning, control of young shoot development during fruit growth, harvesting index, techniques, etc..
Durian fruits almost ready for harvest
Thailand - The Leading Producer and Exporter of Durian
Did you know that the common durian is not indigenous to Thailand but was introduced to central Thailand in 1787 from the South East region of Myanmar and to southern Thailand from Malaysia?
Yet, almost all durian lovers know that Thailand is the leading producer and exporter of durians in the world today. Thai durians are famous for their exotic taste and aroma. If you see a frozen durian in the major cities in European countries, it can only be a Thai durian!
Thailand is blessed with abundant rich soil and climate well-suited to the cultivation of durian. The people involved with the durian industry is hard-working and dedicated. They have developed appropriate technologies over the years to improve durian productivity and quality.
Many of the orchard management practices mentioned in this page are from the English version of the original Thai "Durian Grower's IPM Notebook" for use by extension officers to train durian growers in the Eastern Region of Thailand. This manual is very informative and practical.
The other Thai resource is from a seminar paper "Durian (Durio zibethinus L.) Flowering, Fruit Set and Pruning" written by Surmsuk Salakpetch, Director of Chanthaburi Horticultural Research Center, Chanthaburi, Thailand. Paper presented during the 15th International Tropical Fruit Conference held in Hawaii, October 21-23, 2005.
===================================
The following guidelines and practices are adaptations from the above 2 resources for you to consider and apply in your orchard. The time-line of the different growth stages are generalized for graphic presentations. You will have to adjust the months or growth stages according to the actual situation in your farm.
Please feel free to review and comment on these guidelines and practices.
-----------------------------------------------
Durian production technologies have been developed based upon an understanding of several factors and concepts: the crop (durian), necessary production materials, environmental physiology, source-sink relationships and the interaction between the crop, production materials, environmental physiology and source-sink relationships.
 |
| Durian production in the Eastern Region of Thailand |
 |
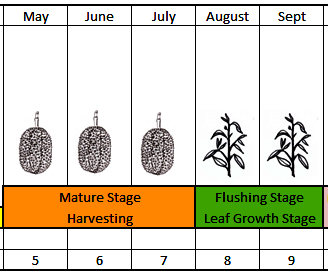
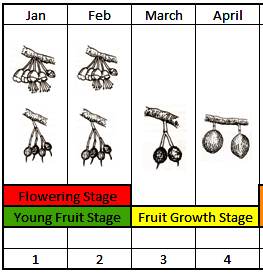
| Durian growth stages and crop production stages in Eastern Region of Thailand |
- Fruit Mature - Harvesting - Post-Harvest Stage
- Flushing Stage - Leaf Growth Stage
- Durian Tree Preparation - Flowering Stage
- Recovery Stage - Food Collection
- Flowering Initiation Stage
- Flowering - Young Fruit Stage
- Fruit Growth Stage
Crop Proction Cycle: 1.Mature - Harvesting and
2. Leaf Flushing and Growth Stages
1. Fruit Mature - Harvesting - Post-Harvest Stage
(May to July)
Depending on the durian cultivars or clones, the fruits will mature and drop 3-5 months after flowering. In Thailand, most of the mature fruits are harvested manually and then allowed to ripen. In Malaysia, Indonesia and the Philippines, mature fruits ripen on the trees and drop naturally and be collected later. Natural fruit drop usually last about 10 weeks and follows a specific pattern - a few during the first week, then peaking in the second and third week and decreasing again in the later weeks.
 |
| Placing netting under a durian tree to collect ripen durians that fall to the ground |
Immediately after harvesting, complete fertilizer such as 16N-16P2O5 -16K2O and cow manure are applied to strengthen the tree. The damaged, diseased, dried and unused branches should be pruned off to promote the emergence of new shoots.
Manual harvesting of mature durian
a. Harvesting
- Harvest mature fruits at the correct harvesting indices or allow the fruits to drop naturally.
- Harvested fruit should not be placed on the ground to avoid contact with dirt and infection by pathogens.
- Keep records of harvest such as quantity and price.
- Identify good, fair and non-productive trees for further action.
Immediately after the harvest, the durian trees must be pruned and fertilized with equal proportions of NPK fertilizers to prepare the trees for healthy growth.
b. Pruning
- Trim all branches.
- Prune all branches affected by pests and diseases.
- Remove all dead and dry branches.
- Apply copper oxide fungicide as protective/preventive measure at pruned surfaces.
Pruning after the harvest season
c. Applying Fertilizers
Note: Fertilizer ratios and rates suggested in this section are general recommendations. Do not use these guidelines as absolute figures.
- After pruning, apply complete fertilizer with ratio 15:15:15; 16:16:16; or 20:20:20
- Fertilizer amount or rate (usually 2-3 kg/tree) depends on tree vigor.
- Incorporate fertilizers along the canopy drip line.
- Apply organic fertilizer at the rate of 10-20 kg/tree, according to tree size.
- Apply express or foliar fertilizer to immature fruits that are hanging on the trees (See Note).
- Check soil for phytophthera and termites.
Fertilizers placed in pockets around the tree
Fertilizers placed in a trench
along the drip-line
along the drip-line
d. Keeping The Farm Clean
- Burn all dead and dry branches.
- Bury or burn all rotten fruits.
- Dig furrows if have drainage problems.
- Repair irrigation facilities.
- Remove excess weeds.
Note:
(foliar feeding to hasten ripening of immature fruits to complete the harvesting stage)
Express formula 1
- Glucose sugar - 600 g
- Humic acid - 20 cc
- Foliar spray 1:2:1 - 60 g
- Water - 20 litres
Express formula 2
- Malt sugar - 20 cc
- Humic acid - 20 cc
- Foliar spray 15:30:15 - 60 g
- Water - 20 litres
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
2. Leaf Flushing - Leaf Growth Stage (August - September)
Crop Production Cycle: Leaf Flush
A new flush of leaves usually appear after the harvest. If the development of new leaves is poor, or the previous harvest was a good one, increase the nitrogen in the fertilizer applied to the soil, as well as in the foliar sprays. Irrigating the trees frequently to support the development of new leaves is also important. Most Thai farmers use pipe or sprinkler irrigation system not only to deliver water but also water-soluble plant nutrients to the trees.
- Apply nitrogen fertilizers to stimulate leaf flushing.
- Use fertilizer with high N such as 15:0:0: or 46:0:0 at rate of 40-50g/20 litres water. This is added to the irrigation system.
- Apply supplementary plant food or express fertilizers to nourish the leaves.
- Check soil and trees for phytophtera and termites. If necessary take appropriate action(s).
- Apply water if weather is too dry.
Express formula 1
- Glucose sugar - 600 g
- Humic acid - 20 cc
- Foliar spray 1:2:1 - 60 g
- Water - 20 litres
Express formula 2
- Malt sugar - 20 cc
- Humic acid - 20 cc
- Foliar spray 15:30:15 - 60 g
- Water - 20 litres
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
3. Durian Tree Preparation For Flowering Stage (October)
At 2 months before flowering, fertilizers are applied with the aim of:
- helping existing leaves to mature;
- preventing the appearance of new leaves, thus avoiding competition for nutrients; and
- enhancing flower initiation.
Fertilizers at this stage should have high P and K content, and a low N.
In addition to fertilizing the soil, a foliar fertilizer with no N, very high P and K content should be sprayed. Boron should also be applied. Besides using fertilizer, creating a long, dry period just after the completion of leaf development to limit vegetative growth of the tree, and then applying plenty of irrigation water, also helps to enhance flower initiation.
- Apply fertilizers to stimulate flowering.
- Use fertilizers with high P and K, ratios of 9:24:24; 8:24:24; or 12:24:12
- Rate at 2-5 kg/tree depending on tree vigour.
- Prune incomplete branches.
- Check and control branch weevils or stem weevils.
- Do manual weeding of excess weeds - do not use chemical weedicides.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Tree Recovery and Food Collection Stage
- Control water to the trees
- Check and control red-mites or weevil outbreaks
- If too many flowers on branches, cut off excess flowers at end of branches.
Crop Proction Cycle: Tree Preparation for Flowering to Flowering Stages
Crop production Cycle: Young flower buds
Flowering Initiation Stage
- Do flower thinning if too many flowers.
- Keep flowers of the same age, and cut off the rest.
- When flower buds are at fish-egg size, increase water supply.
- Reduce water when flowers open.
- If heavy winds, continue with watering, do not stop watering.
- Check and control red-mites, spray water to increase humidity to control red-mites
- Use chemical propagyte if heavy red-mite attack
Durian flowers and blooming
Fruitlets
Flowering - Young Fruit Stage
- Reduce watering to one-third of normal supply before flower opening 7 - 10 days.
- After that increase water to correlate with fruit growth.
- Do durian pollination.
- Check/control flower wilt or dry pollens.
- Record flowering opening date for estimate next harvesting.
- Thin young fruits at end of branches.
Crop Production Cycle: Flowering to Fruit Growth Stages
Fruit Growth Stage
Durian Fruitlets
To improve the size and general quality of the fruit, fertilizer should be applied to the soil as awell as in the form of a foliar spray. NPK fertilizer 1:1:1.5 should be applied to the soil. The foliar spray should have a high K content.
- Increase water 10% of normal water supply.
- Thin small fruits or irregular-shaped fruits.
- If strong winds or dry weather, increase water supply.
- Apply fertilizers to nourish fruits/leaves.
- Fertilizer ratio 12:12:17:2 or 4:16:24:4 at 2-3 kg/tree at 60 days after flowering open.
- Apply potassium sulphate 50% at rate 0.5 kg/tree at 30-45 days before fruit ripens.
- Apply express formula on incomplete leaves with glucose sugar, humic acid or foliar spray 1:2:1; or 15:30:15.